Ransomware
Overview
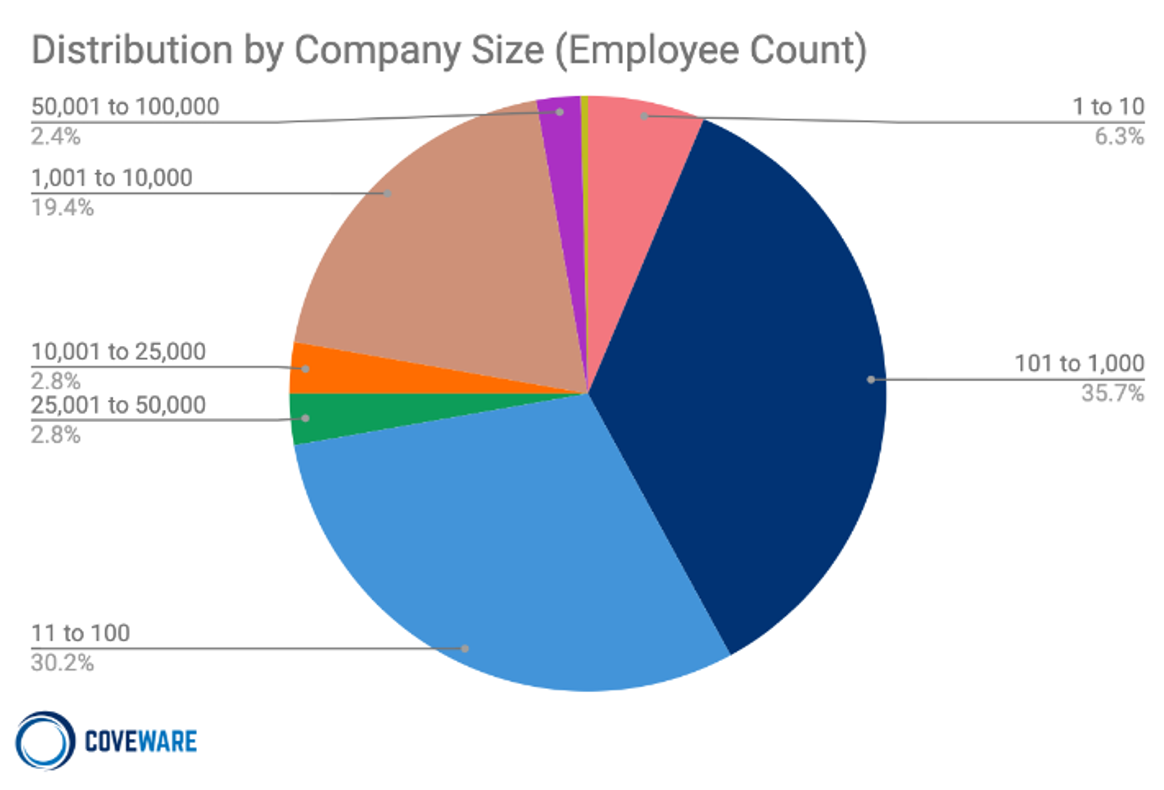
Ransomware is a huge global threat to businesses around the world. The high-profile attacks are well-known: Colonial Pipeline, JBS, Garmin, Acer. But many people now know a colleague whose small business was attacked, because the majority of corporate targets are small and medium businesses. According to Coveware, 72% of targeted businesses have fewer than 1,000 employees, and 37% have fewer than 100. These aren’t large corporations with the resources to plan for this vector of attack. These are small businesses that have one or two IT administrators on staff or even no in-house IT. Businesses are projected to pay out $20B in 2021, a 100% Y-o-Y increase for the last four years, and it’s only going to get worse with new business models like RaaS: ransomware-as-a-service.
The problem for companies is that their storage is always connected with full access for admins. When ransomware gets the administrative credentials, it has full access too. There is no policy to say that no one, not even the administrator, can change this file for a set amount of time. Ransomware attacks are increasingly sophisticated, having the capability of watching for cloud account credentials, deleting backups and cloud storage, then encrypting everything and demanding a ransom. It’s imperative to build defenses against these escalating attacks.
SMBs and large businesses need two layers of defense:
- Protection: A backup target that allows them to lock backups for a designated time period for immutable backups.
- Detection: An algorithm for detecting changes in the source volumes that is outside of expected variance.
Protection: Immutable Backups
Cloud Object Lock locks files for a period of time. Because cloud storage providers like Amazon S3 control the API, they can add features like Object Lock, also referred to as Write-Once-Read-Many (WORM) storage or immutable storage. This lock is a retention policy for a specific version of a file that is locked from changes from every user, including the administrator. You can think of this as a virtual air-gap in the cloud because there is no way, barring to close the account, to delete that file before the retention date is passed.
Retrospect Backup uses Object Lock to create Immutable Backups. These backups are locked for a specific amount of time. Users can set a retention period for backups stored on supporting cloud platforms. Within this immutable retention period, backups cannot be deleted by any user, even if ransomware or a malicious actor acquires the root credentials.
Using ProactiveAI for advanced scheduling logic, Retrospect provides a rolling window of immutable backups, combining forever-incremental backups with point-in-time restores even after the initial backup passes out of the immutable retention policy.
Retrospect Backup’s ransomware protection is certified with Amazon S3, Microsoft Azure Blob Storage, Google Cloud Storage, Wasabi, Backblaze B2, and MinIO.
For more information about ransomware protection with Retrospect Backup, see Ransomware Protection.
Detection: Anomaly Detection
Organizations need to detect ransomware as early as possible to stop the threat and remediate those resources. Anomaly Detection in Retrospect Backup identifies changes in an environment that warrants the attention of IT. Administrators can tailor anomaly detection to their business’s specific systems using customizable filtering and thresholds for each of their backup policies, and those anomalies are aggregated on Retrospect Management Console across the entire business’s Retrospect Backup instances or a partner’s client base with a notification area for responding to those anomalies.
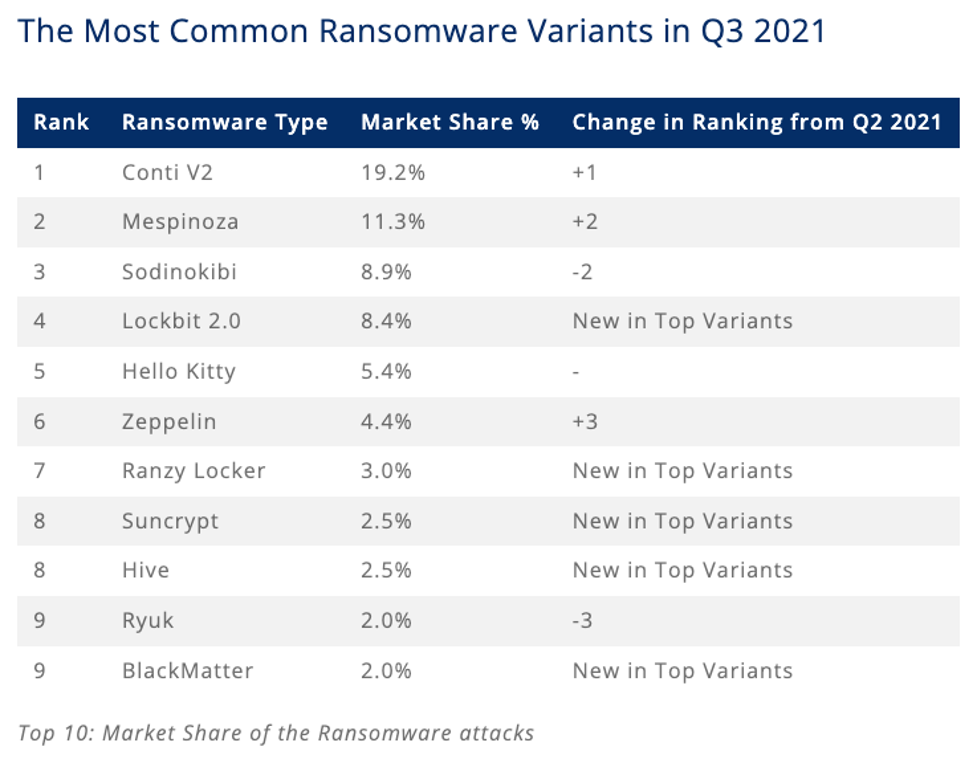
Retrospect Backup detects all of the major ransomware variants using an algorithm that focuses on file metadata anomalies. According to Coveware, the top variants are always changing, with over 50% changing every quarter. The key to detection is combining technologies such as signature detection in processes with file-based irregularities. Using a multi-pronged defense, with immutable backups, anomaly detection, and other security layers, businesses will know when they’re being attacked and will have the tools to remediate it and move on.
For more information about anomaly detection with Retrospect Backup, see
Last Update: February 15, 2022