Ransomware

Google Cloud Storage provides a low-cost, scalable cloud storage location for secure off-site data protection. With its Bucket Lock retention policy, Google Cloud enables customers to lock files that are under a certain age in that bucket. PDF version also available.
This per-bucket policy approach differs from Amazon S3’s per-object policy approach, such that Retrospect Backup cannot set the retention policies for individual files that make up a backup. However, setting a bucket policy enables customers to lock the files for a certain period of time, so this is a great Ransomware solution for Google Cloud customers.
Overview
Ransomware attacks are increasingly sophisticated, having the capability of watching for cloud account credentials, deleting backups and cloud storage, then encrypting everything and demanding a ransom. It’s imperative to build defenses against this escalating attack. SMBs and large businesses need a backup target that allows them to lock backups for a designated time period. Many of the major cloud providers now support object locking, also referred to as Write-Once-Read-Many (WORM) storage or immutable storage. Users can mark objects as locked for a designated period of time, preventing them from being deleted or altered by any user.
Backups made to a Google Cloud Bucket with a retention period are immutable backups, with a retention period that prevents deletion by anyone accessing the bucket.
Note that customers are responsible for keeping track of the retention period and modifying it accordingly to ensure all of the backups inside the bucket continue to be marked as immutable backups.
For more information about backing up to Google Cloud Storage with Retrospect Backup, see
Step-by-Step Guide
Retrospect Backup makes it easy to back up to Google Cloud Storage. Let’s walk through the steps for creating a bucket with a Bucket Lock retention policy.
- Retrospect: Add a destination. On Windows, select "Backup Sets" then "Create". On Mac, select "Media Sets" and click "Add". Select type "Cloud".
- For an existing bucket, type in the appropriate path and credentials. Note that the "Immutable Retention Policy" checkbox is not relevant because you’ll use the Google Cloud Storage bucket with the bucket-level retention policy. Be sure that retention is configured on the bucket.
- For a new bucket, type in the Google Cloud Storage URL and the appropriate credentials and append the name of the bucket you’d like to create: storage.googleapis.com/this_is_my_new_bucket. Retrospect will attempt to create the bucket with immutability enabled if you have the option set.
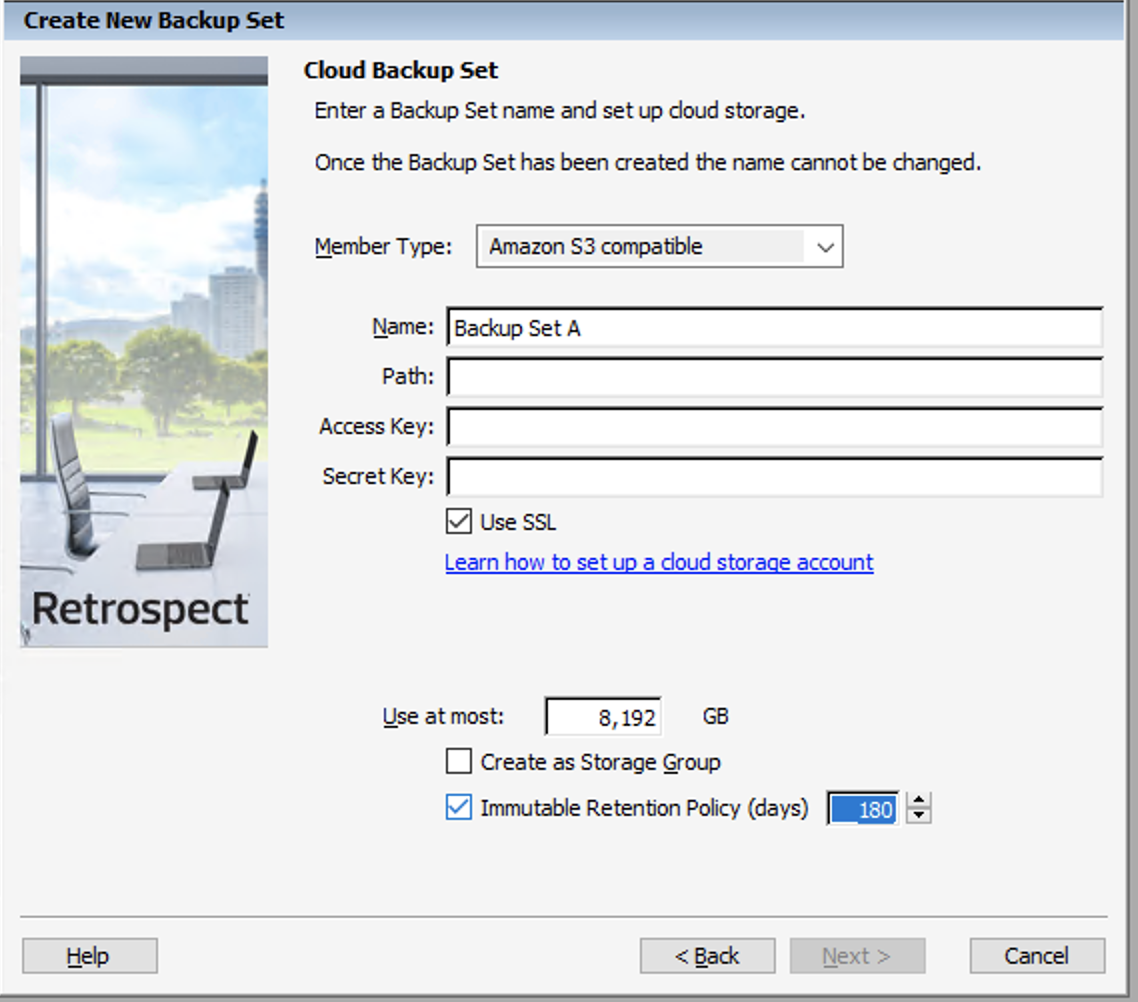
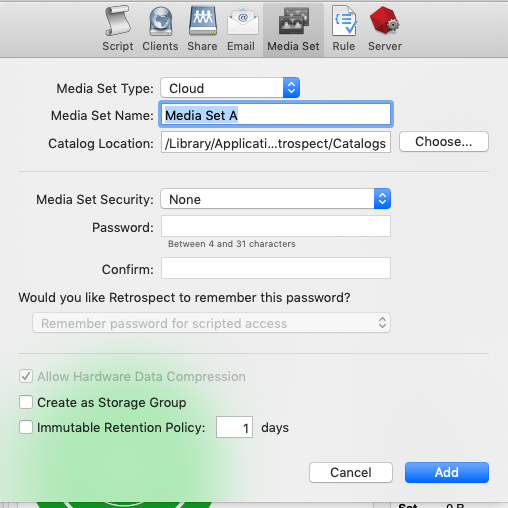
Retrospect: Add the destination to a script and start protecting your data in Google Cloud Storage.
Google Cloud Console
To create a bucket using Google Cloud Console:
Google Cloud Storage:
Google Cloud Storage: Click "Create Bucket".
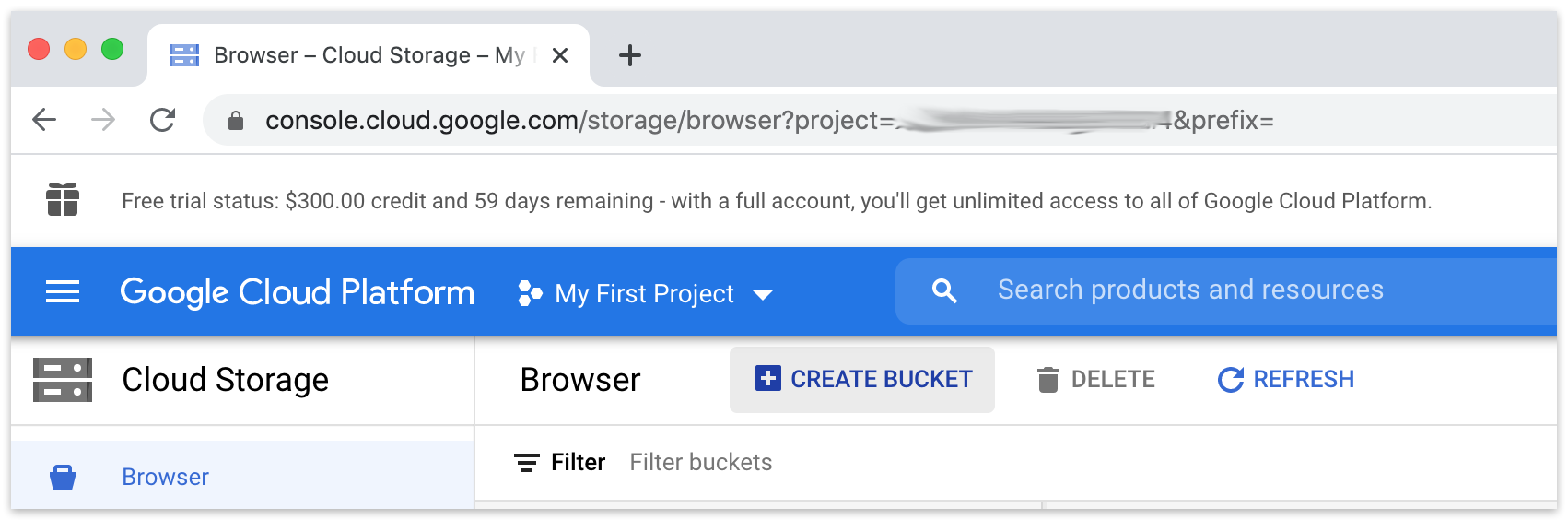
Google Cloud Storage: Enter a bucket name.
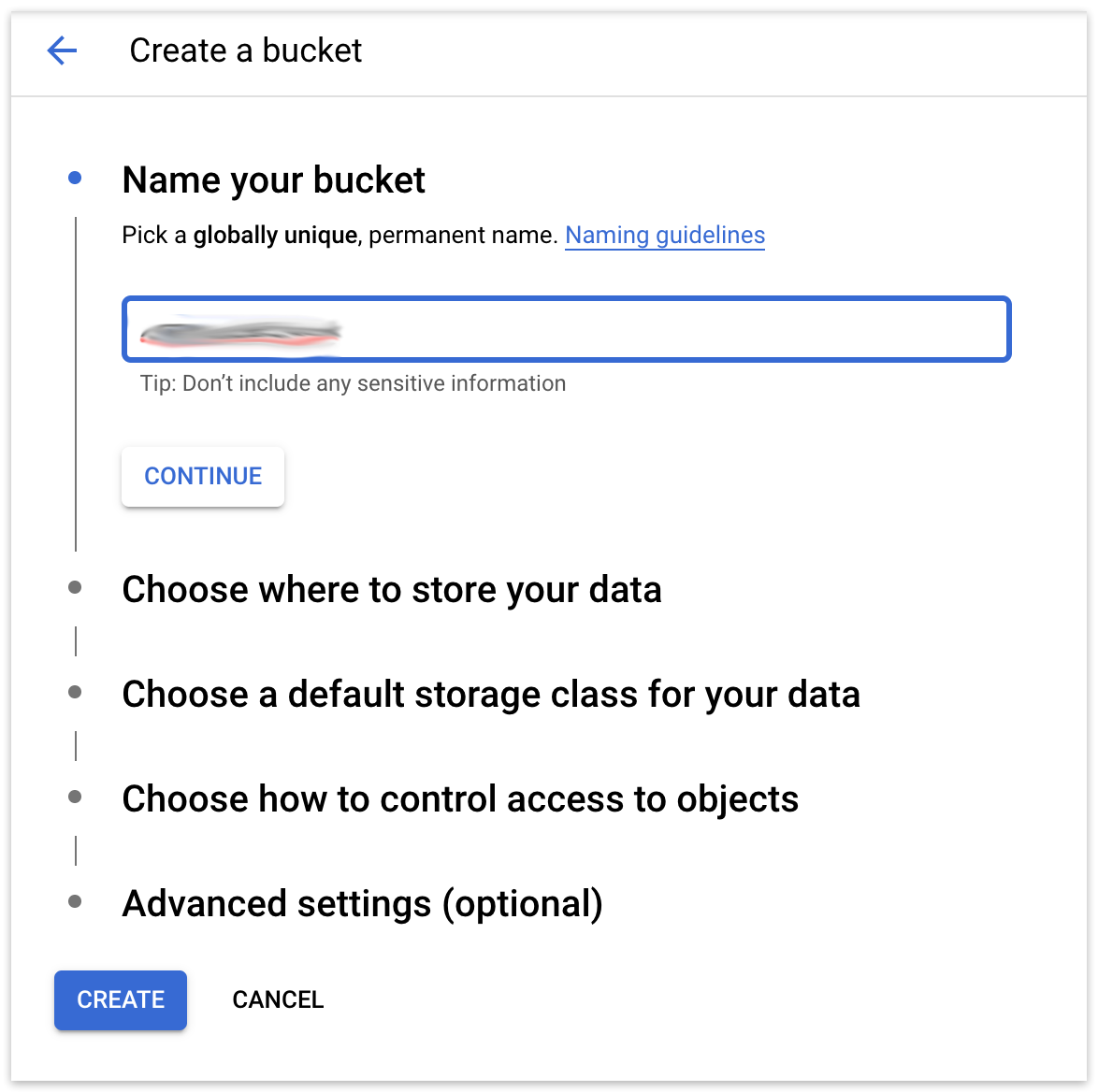
Google Cloud Storage: Under "Advanced Settings", you’ll see "Retention policy". Enable "Set a retention policy" and enter a time period.
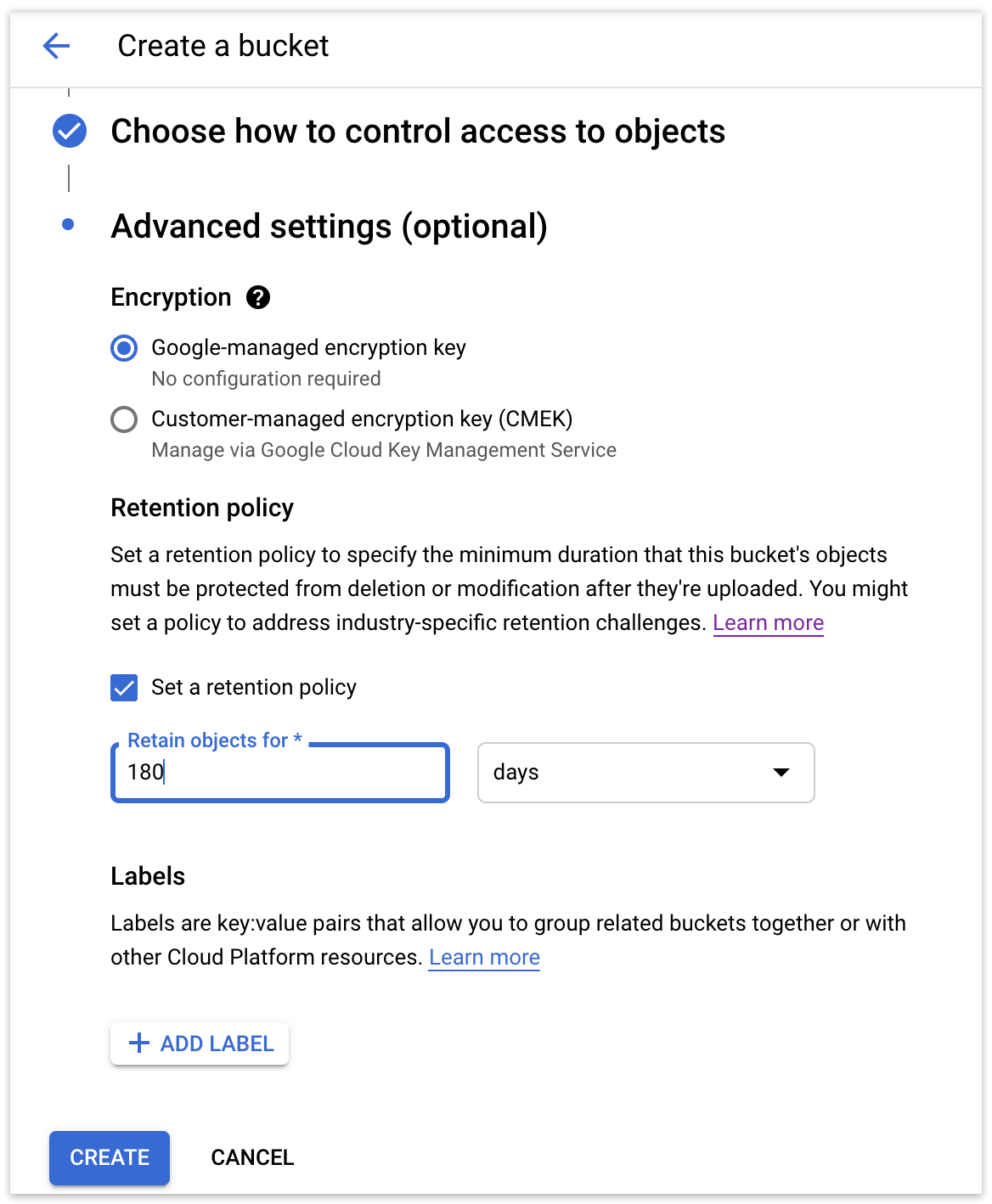
Google Cloud Storage: Finish setup and create the bucket.
Google Cloud Storage: In the bucket, under "Retention", you’ll see the policy you set up.
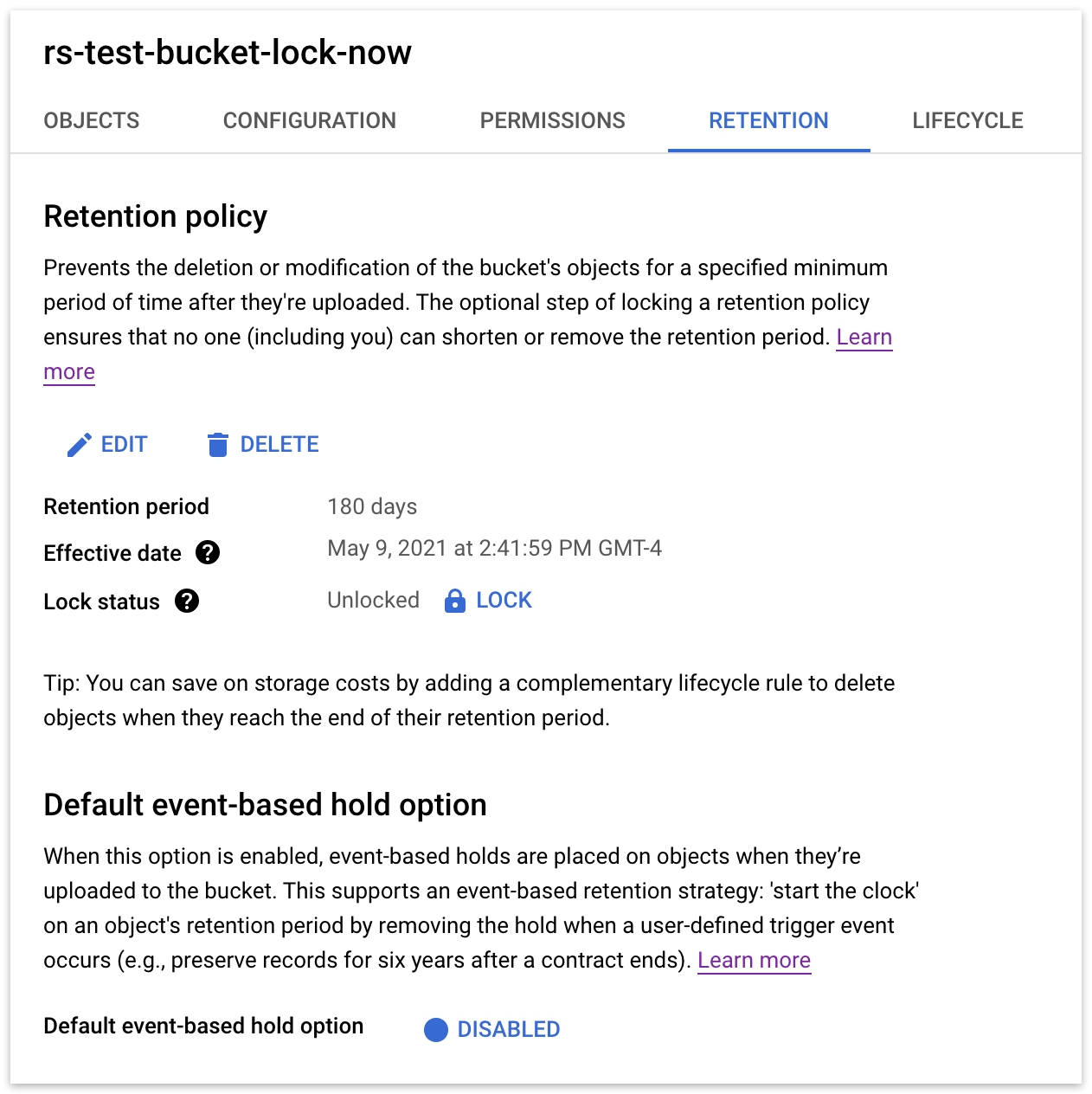
Note that you need to click "Lock" to make the retention policy effective. Once you lock it, you cannot unlock it until all objects are out of the retention period.
Under The Hood
Every backup within the retention period is an immutable backup with point-in-time restore capabilities. Because each backup is incremental, Retrospect only transfers the files that are new or have changed since the last backup. However, you can always restore any part of a backup in Retrospect.
Google Cloud Storage will mark every new backup file with the specified retention policy, protecting your backups from any accidental or malicious deletion. However, you are responsible for ensuring none of the backup files fall out of the retention period, as Google Cloud Storage does not provide the ability to change individual file’s retention periods.
Last Update: February 15, 2022