White Papers
With the availability of on-premise storage, private cloud locations, and public cloud infrastructure, companies have a variety of choices for how to store and access their critical data. Selecting the correct tier for the particular data is an optimization between accessibility, retrieval speed, and cost.
On-premise NVMe storage, including Nexsan V-Series, provides extremely fast access to data at a high cost, while large disk arrays, including Nexsan E-Series, deliver on-premise access to low-cost scalable storage. Public cloud providers offer a rich set of storage tiers as well, ranging from fast and always available to very affordable with a flexible retrieval time period.
Leveraging cloud storage allows companies to lift-and-shift sections of their data to the cloud, adding redundancy through public cloud providers' built-in infrastructure and reducing on-premise costs.
Retrospect Backup enables data migration and replication between on-premise storage and off-premise cloud storage using policies that can be scheduled with advanced filtering capabilities. With Retrospect, companies can replicate their data local-to-cloud, cloud-to-local, and cloud-to-cloud with certified support for Amazon S3, Microsoft Azure Blob Storage, Google Cloud Storage, Backblaze B2, Wasabi, and MinIO. Let’s walk through how.
Adding Cloud Storage
In Retrospect, click on "Volumes" (Windows) or "Sources" (Mac).
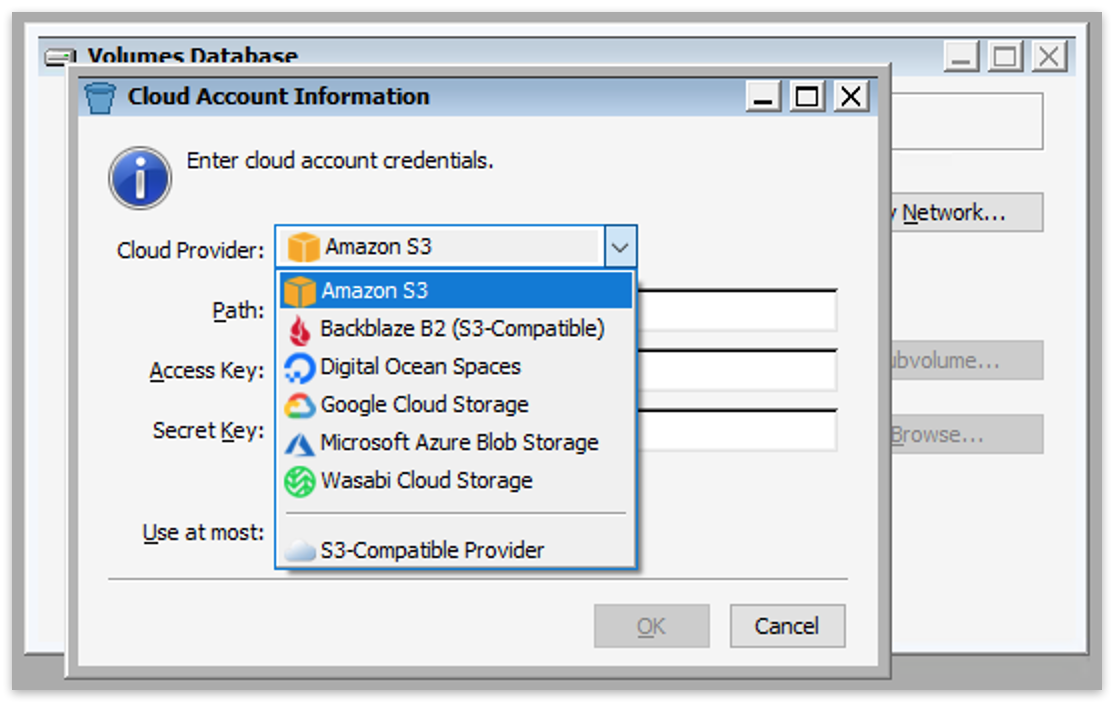
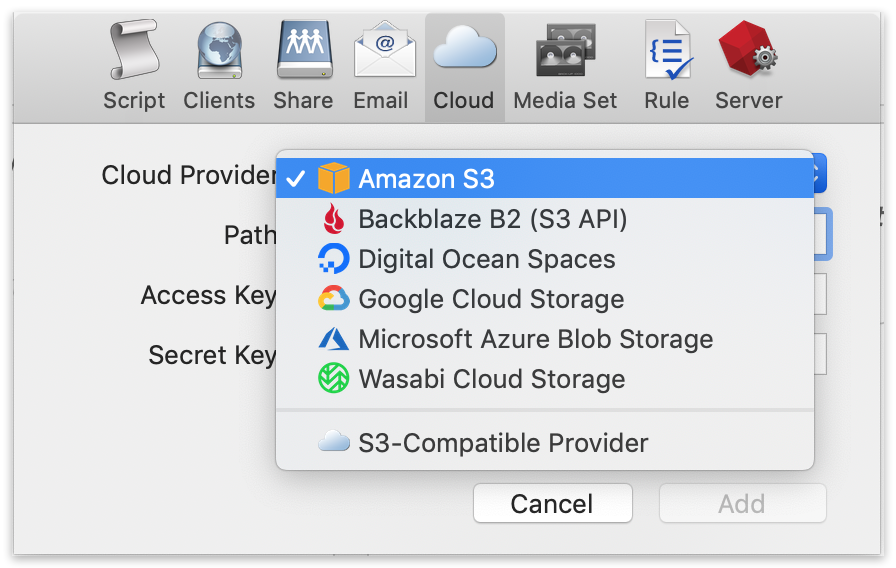
Select "Amazon S3" or your preferred provider.
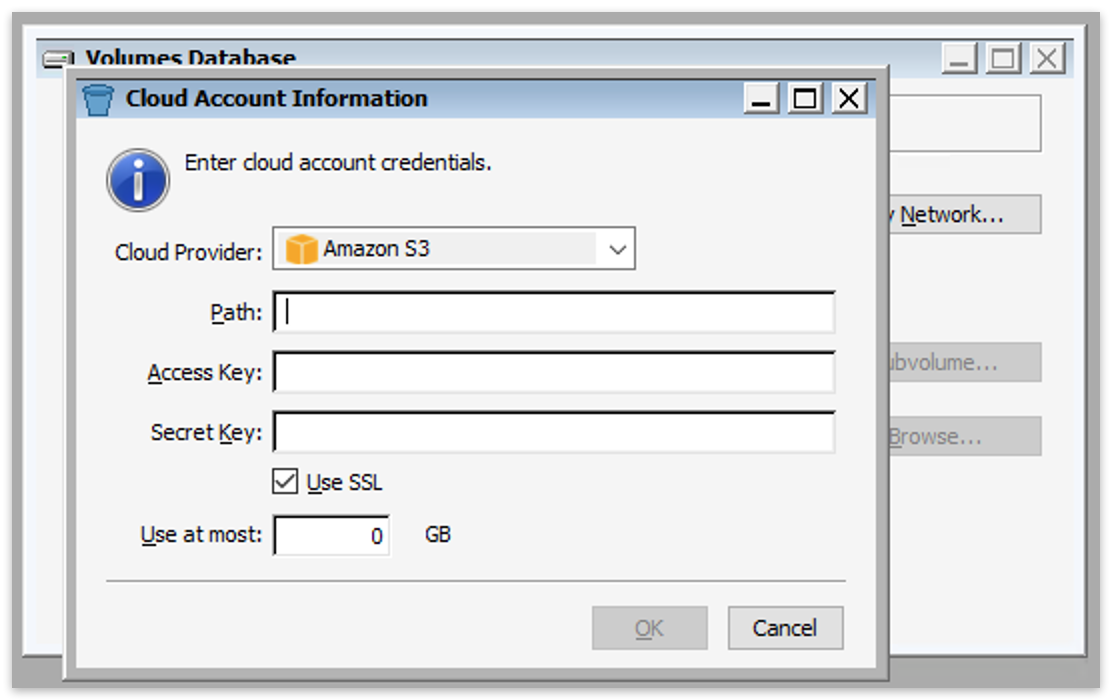
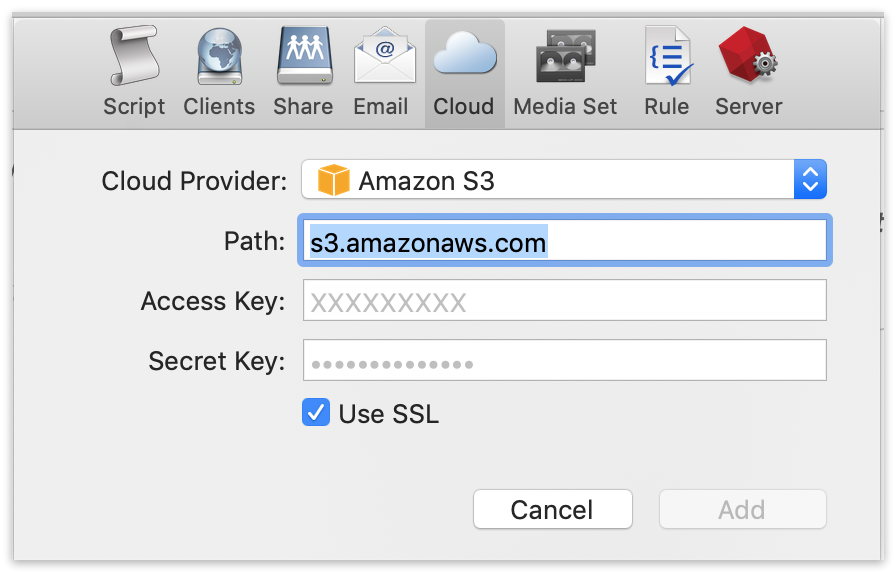
Type in your path information and credentials from above and click "OK".
We now have a cloud storage volume added to Retrospect. We can replicate it or from it or even back it up. For more information about protecting cloud storage with on-premise backups, see
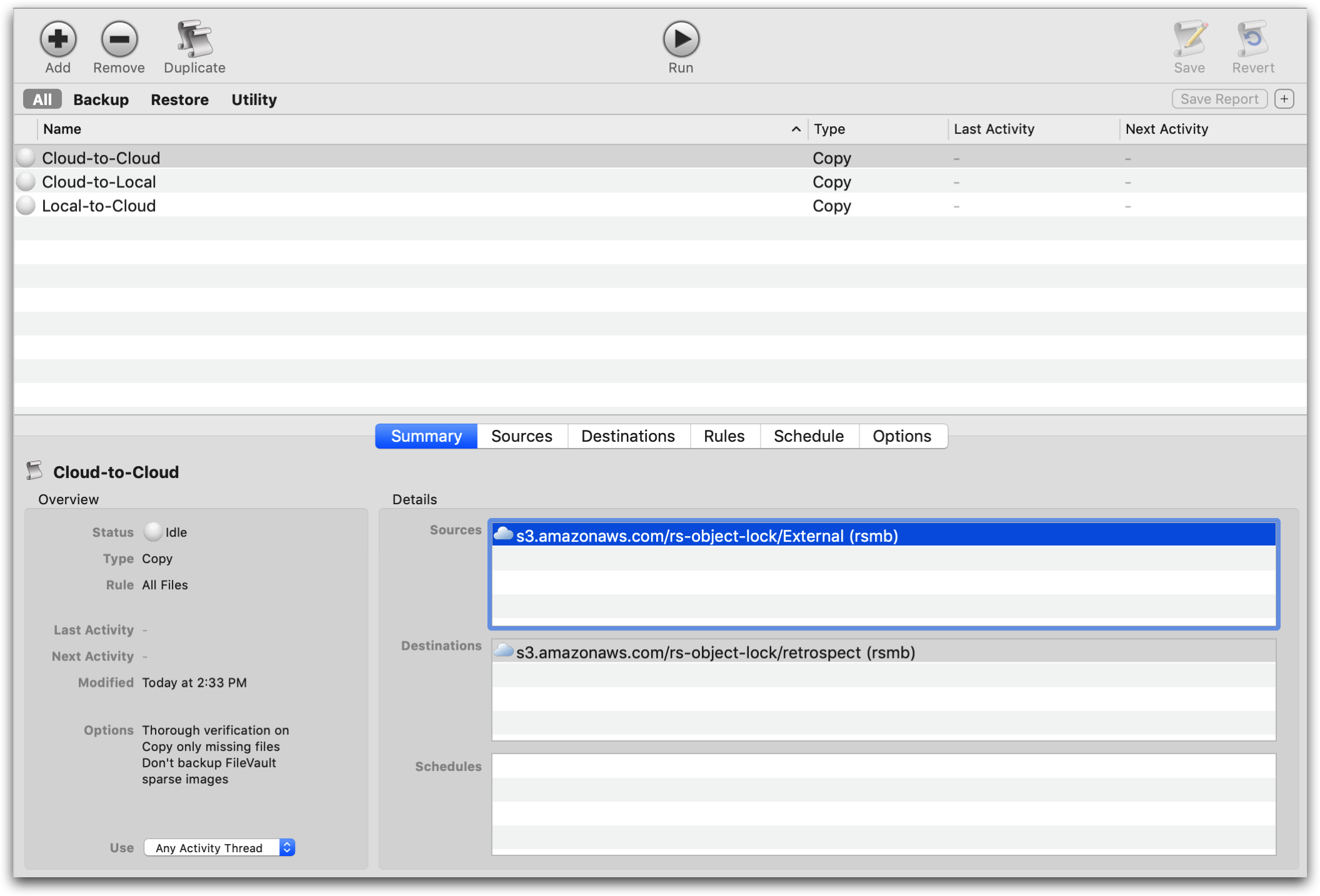
Replication Policies
To create a replication policy:
Select "Scripts".
Click "New" (Windows) or the plus button (Mac).
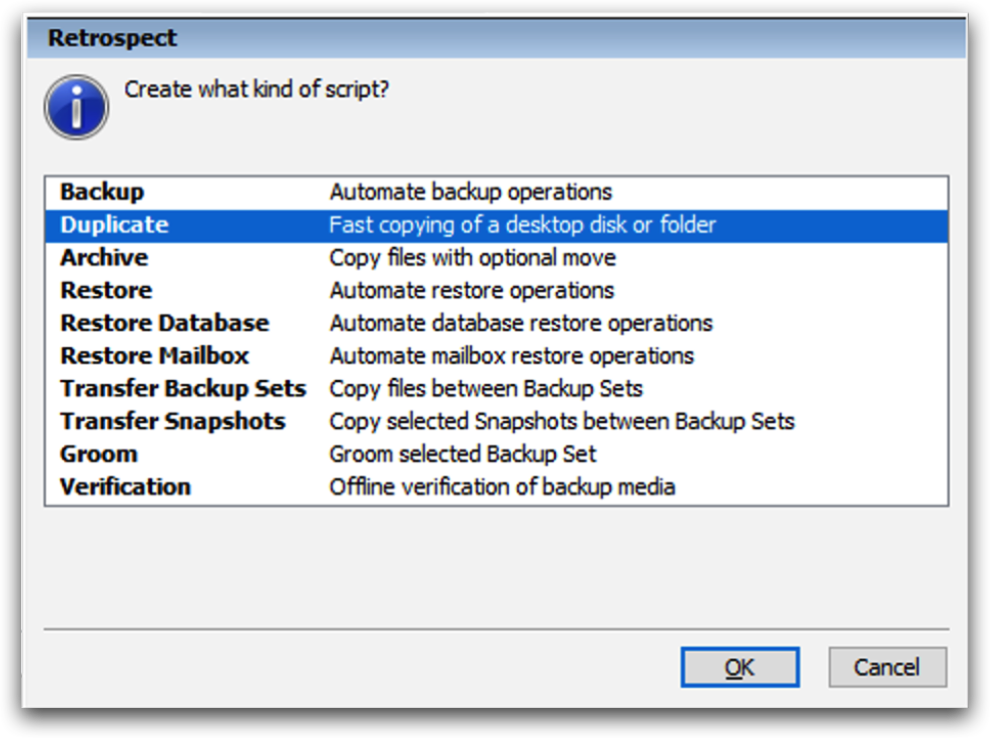
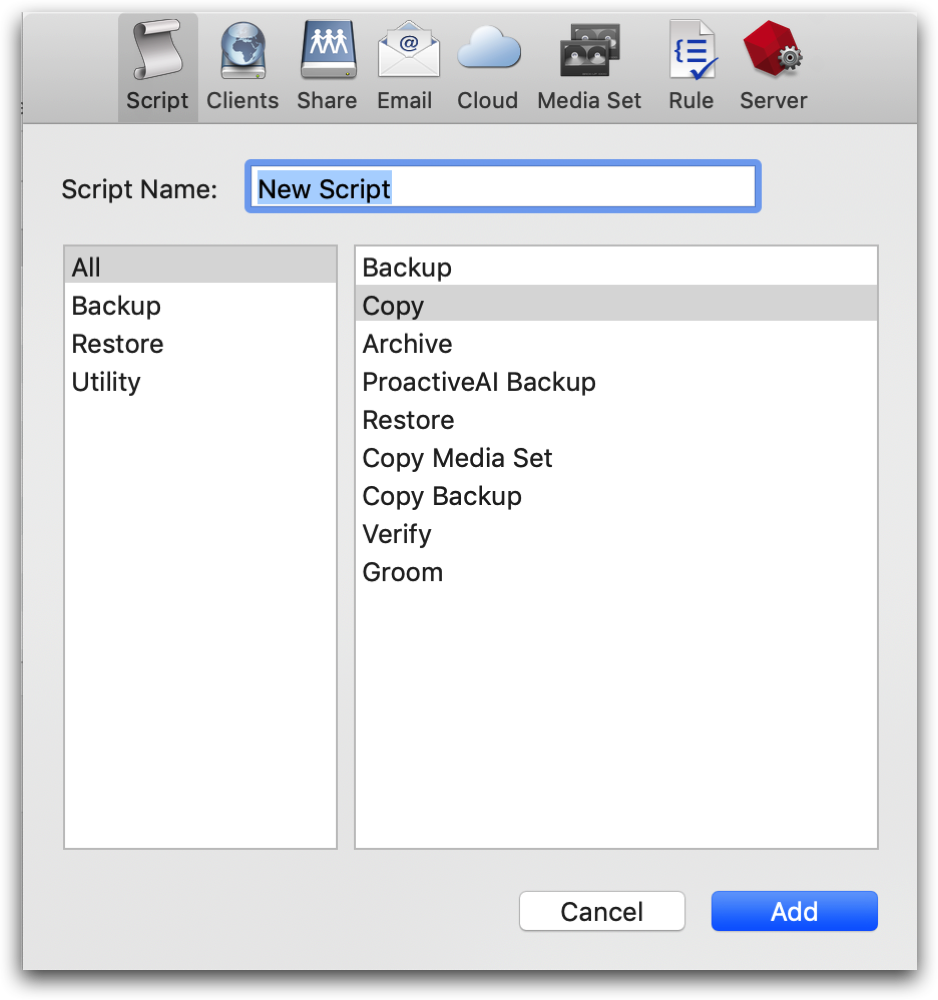
Select "Replication" (Windows) or "Copy" (Mac).
Now that we have a policy, we can set it up.
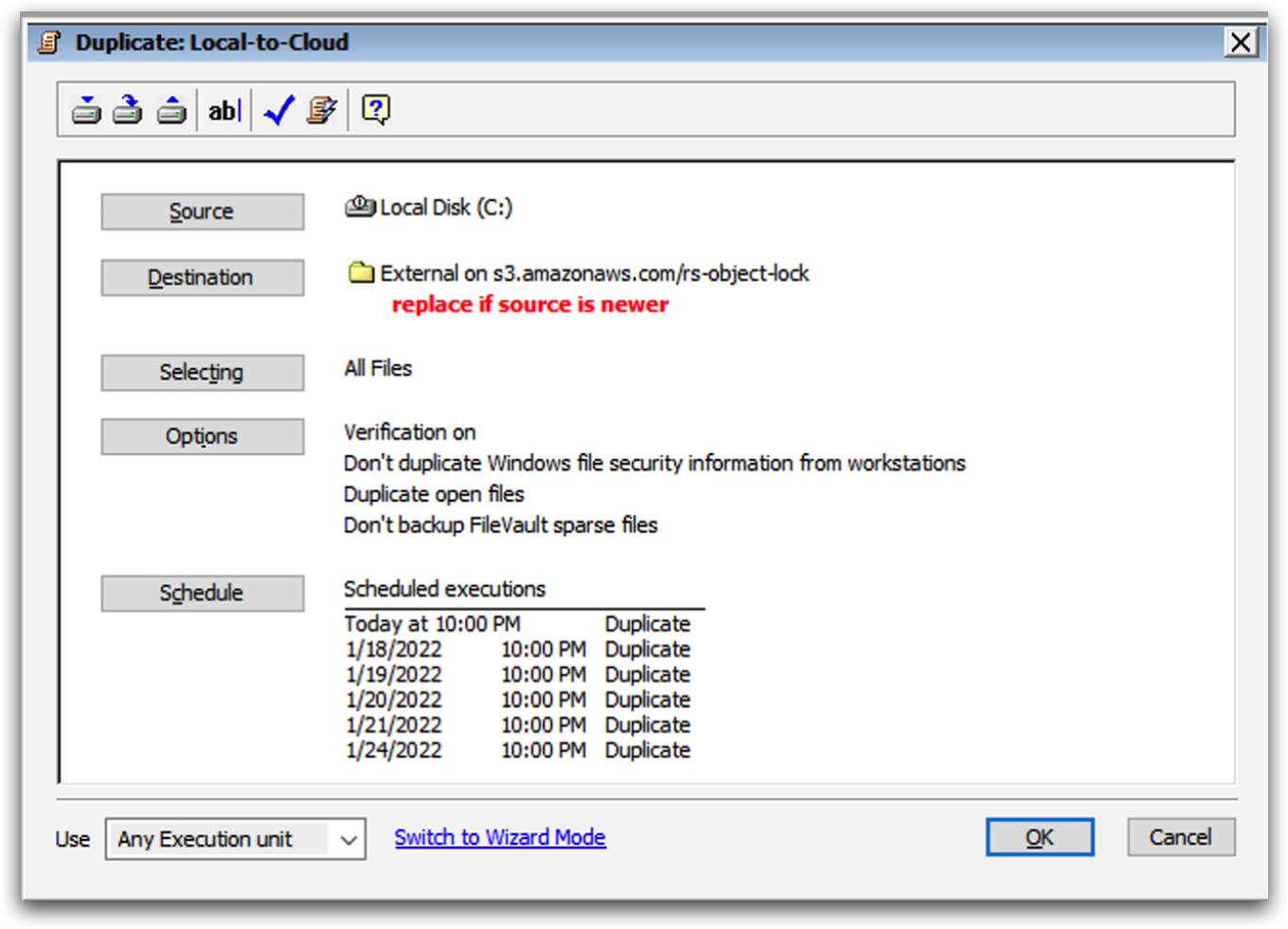
Local-to-Cloud Replication
To replicate from a local volume to a cloud volume, add the local volume as the source and the cloud volume as the destination.
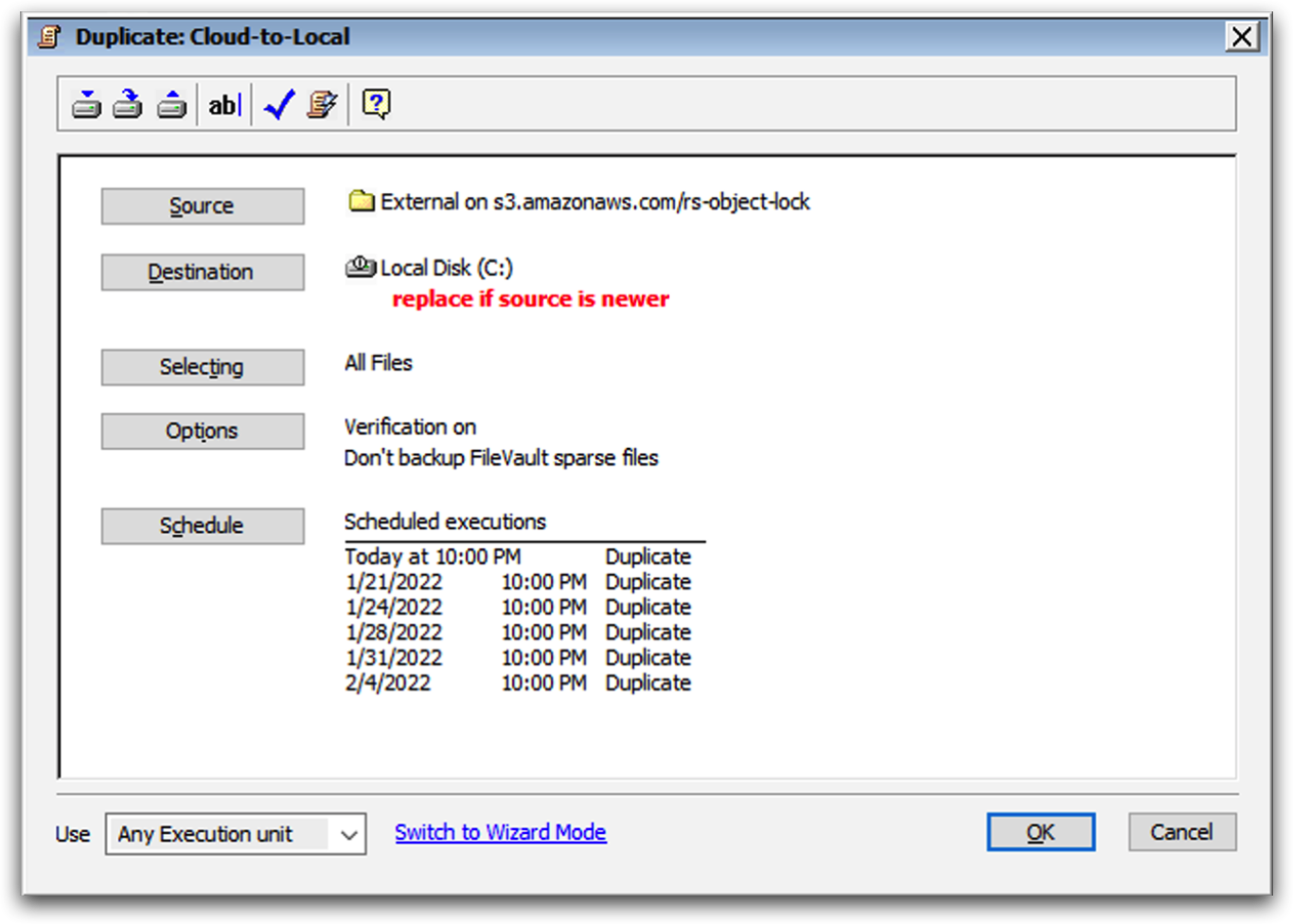
Cloud-to-Local Replication
To replicate from a cloud volume to a local volume, add the cloud volume as the source and the local volume as the destination.
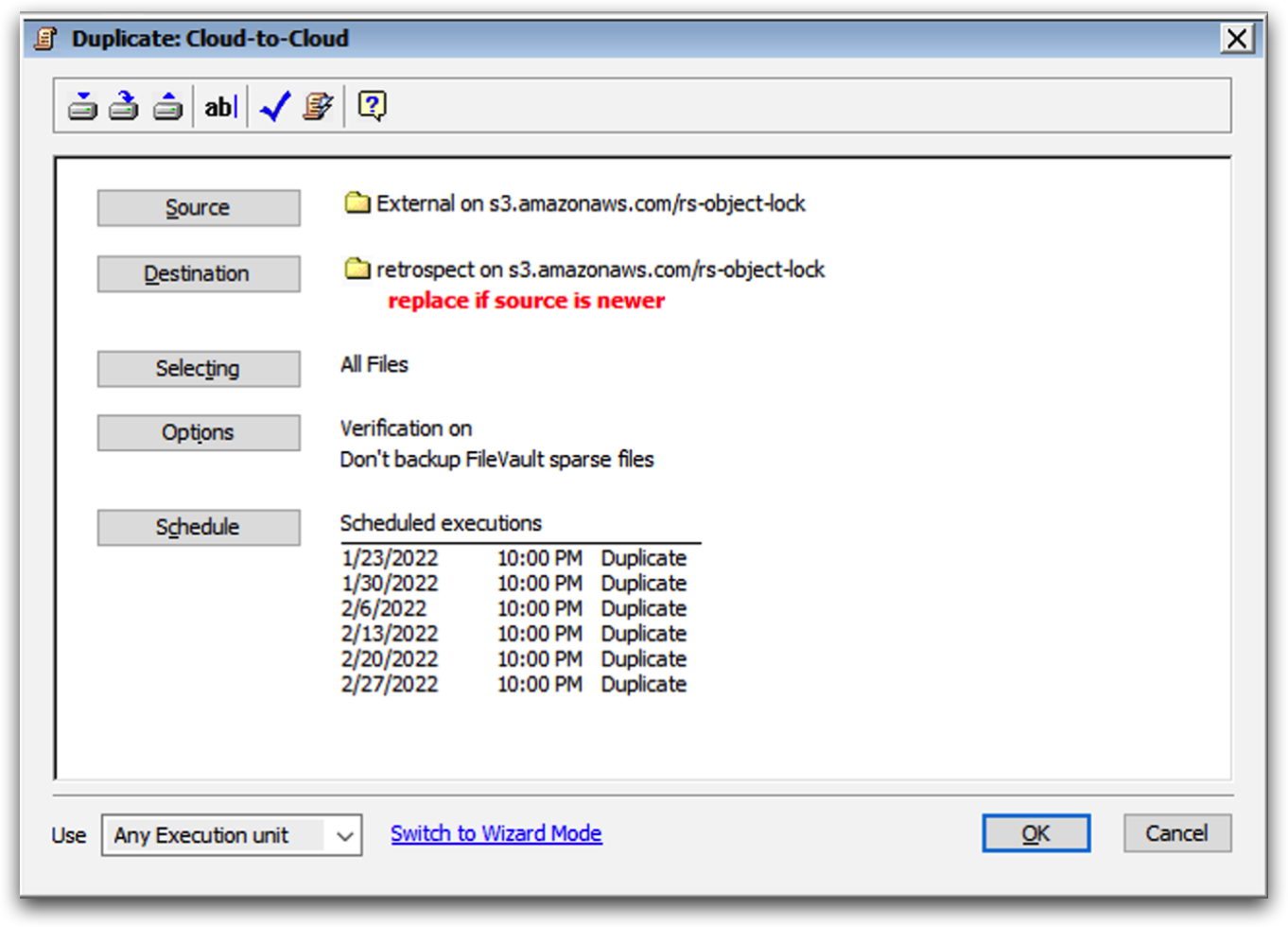
Cloud-to-Cloud Replication
To replicate from a cloud volume to a different cloud volume, add the first cloud volume as the source and the second cloud volume as the destination.
Last Update: January 17, 2022